 email: info@shiva-electronics.com
|
email: info@shiva-electronics.com
|
 email: photosw_nsk@sancharnet.in
|
email: photosw_nsk@sancharnet.in
|
 +91-253-6566565
+91-253-6566565
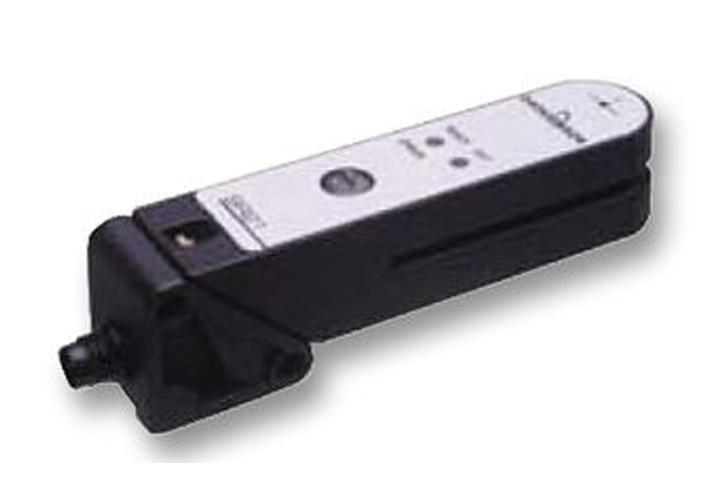

Slot Sensors also called as Fork Switches because of their forked shape, detect objects that pass between the two
arms one is the Transmitter & the other is the Receiver. These sensors operate on a through beam design, they
combine the transmitter & receiver into a fixed housing so alignment is never an issue. The transmitter emits
pulsed light in the infrared wavelength range. The receiver detects the light beam and immediately converts a
beam interruption caused by an object in the sensing zone into a switched signal. Fork Width is defined as the
height between the transmitter & receiver. Depth is defined as the distance between the transmitter & receiver
area and back of the opening.
The primary benefits of using fork sensors are easy installation, high immunity to ambient light & ability to detect
different kinds of material. Sensors with different fork widths are available. They are typically used in labeling
applications to detect the presence of the label compared to the carrier material. By adjusting the sensitivity with
the help of a potentiometer or teach-in button, even slight differences in the light attenuation are detected. There
are many applications beyond the packaging industry for fork sensors that include conveyors, small parts detection
and general manufacturing.
Specs Sheet Attached

